Zabbix architecture
In this chapter, we will walk through the process of installing the Zabbix server. There are many different ways to setup a Zabbix server. We will cover the most common setups with MariaDB and PostgreSQL on RHEL- and SLES-based distro's and Ubuntu.
Before beginning the installation, it is important to understand the architecture of Zabbix. The Zabbix server is structured in a modular fashion, composed of three main components, which we will discuss in detail.
- The Zabbix server
- The Zabbix web server
- The Zabbix database
Creation of DB users
In our setup we will create 2 DB users zabbix-web and zabbix-srv. The
zabbix-web user will be used for the frontend to connect to our zabbix database.
The zabbix-srv user will be used by our zabbix server to connect to the database.
This allows us to limit the permissions for every user to only what is strictly
needed.
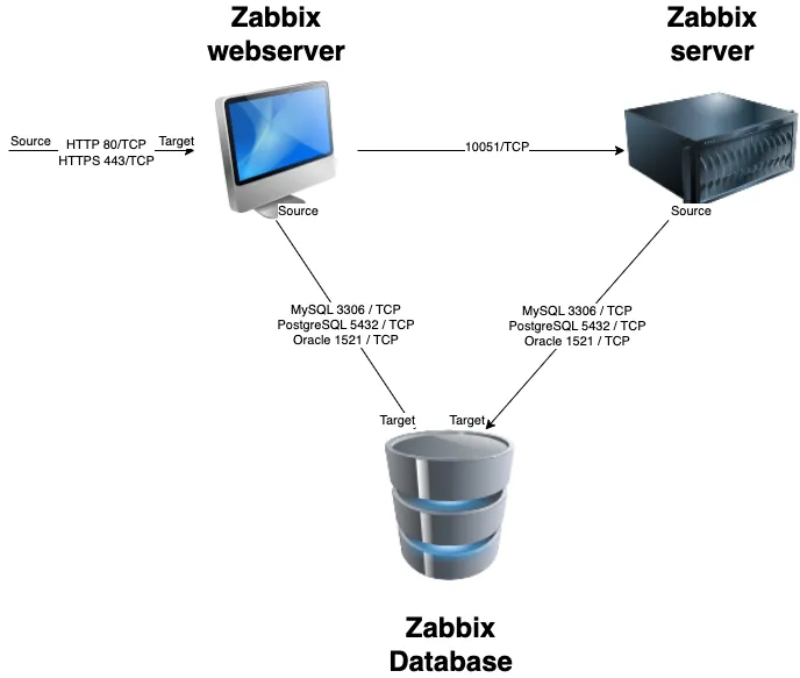
1.1 Zabbix basic split installation
All of these components can either be installed on a single server or distributed across three separate servers. The core of the system is the Zabbix server, often referred to as the "brain." This component is responsible for processing trigger calculations and sending alerts. The database serves as the storage for the Zabbix server's configuration and all the data it collects. The web server provides the user interface (front-end) for interacting with the system. It is important to note that the Zabbix API is part of the front-end component, not the Zabbix server itself.
These components must function together seamlessly, as illustrated in the diagram above. The Zabbix server must read configurations and store monitoring data in the database, while the front-end needs access to read and write configuration data. Furthermore, the front-end must be able to check the status of the Zabbix server and retrieve additional necessary information to ensure smooth operation.
For our setup, we will be using two virtual machines (VMs): one VM will host both the Zabbix server and the Zabbix web front-end, while the second VM will host the Zabbix database.
Note
It is perfectly possible to install all components on one single VM or every component on a separate VM. The reason why we split the DB in our example is because the database will probably be the first component giving you performance headaches. It is also the component that needs some extra attention when we split it from the other components, so for this reason we have chosen in this example to split the database from the rest of the setup.
We will cover the following topics:
- Install our Database based on MariaDB.
- Install our Database based on PostgreSQL.
- Installing the Zabbix server.
- Install the frontend.